Ideal for fall gardens, pansies offer a colorful display for almost six months – in the fall when they are planted, in the winter during a stretch of sunny days and again in spring! Winter pansies may be planted anytime starting in mid-September and continuing through October. Multiple plantings spaced a week or two apart can also ensure even more blooms to enjoy throughout otherwise drab months.
Planting Pansies
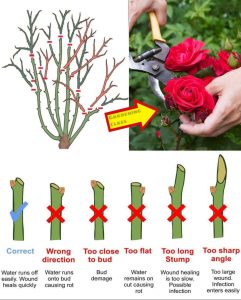
As with any plant, pansies perform better if the soil that you place them in is well prepared. Choose a planting location that is well-drained and work in 4-6 inches of rich organic matter, such as garden compost, peat moss or Bumper Crop. Plant pansies at about the same level, or slightly higher, than they were growing in their market packs or containers, taking care not to plant too deep or the plants may wilt and rot and the roots could smother. After planting, mulch and water the bed thoroughly. Remember to check the plants often during the first three weeks after planting or until new growth begins, to ensure adequate moisture necessary for healthy growth. Because these plants require very little care, no other maintenance is usually necessary for them to reach their full potential.
Where to Plant Pansies
These versatile blooms can be used in many different parts of your garden or landscape. Add a graceful drift of single-colored pansies or a mass of mixed colors to brighten a border, under a tree or along a fence, pathway, deck or wall. Try tucking single plants in garden beds around perennials and shrubs that have finished blooming to brighten up an otherwise dreary section of the landscape and to help mask older, spent growth. Pansies also do well in containers placed on a deck or patio or next to the entrance of your home to greet your guests with welcoming color. Try pansies in a hanging basket and you can even move them indoors to enjoy when the weather is too poor for outdoor gardening. A small container of fall pansies can also be a great gift for winter holidays, birthdays or just to brighten the day of anyone who could use a touch of color in their life.
With so much color to enjoy in so many ways, fall and winter pansies should be a staple of any garden and will bring great gardening joy to the landscape even during colder, dreary months.